YOLOV5损失函数计算
云深安小生 人气:0摘要:
神经网络的训练的主要流程包括图像输入神经网络, 得到模型的输出结果,计算模型的输出与真实值的损失, 计算损失值的梯度,最后用梯度下降算法更新模型参数。损失函数值的计算是非常关键的一个步骤。
本博客将对yolov5损失值的计算过程代码的实现做简要的理解。
def compute_loss(p, targets, model): # predictions, targets, model
device = targets.device
lcls, lbox, lobj = torch.zeros(1, device=device), torch.zeros(1, device=device), torch.zeros(1, device=device)
tcls, tbox, indices, anchors = build_targets(p, targets, model) # targets
h = model.hyp # hyperparameters
# Define criteria
BCEcls = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.Tensor([h['cls_pw']])).to(device)
BCEobj = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.Tensor([h['obj_pw']])).to(device)
# Class label smoothing https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.04103.pdf eqn 3
cp, cn = smooth_BCE(eps=0.0)
# Focal loss
g = h['fl_gamma'] # focal loss gamma
if g > 0:
BCEcls, BCEobj = FocalLoss(BCEcls, g), FocalLoss(BCEobj, g)
。。。。。。
yolov5代码用IOU指标评价目标框和预测框的位置损失损失。yolov5代码用nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss或FocalLoss评价目标框和预测框的类损失和置信度损失 .
yolov5代码用宽高比选择对应真实框的预测框,且每一个真实框对应三个预测框 。
1、位置损失
yolov5代码用IOU值评价预测框和真实框的位置损失, 本文介绍CIoU指标.
公式如下截图:

公式中参数代表的意义如下:
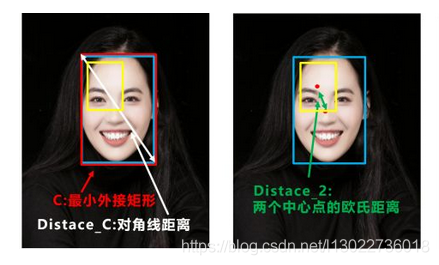
IOU: 预测框和真实框的叫并比
v是衡量长宽比一致性的参数,我们也可以定义为:
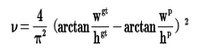
代码实现:
iou = bbox_iou(pbox.T, tbox[i], x1y1x2y2=False, CIoU=True) # iou(prediction, target)
lbox += (1.0 - iou).mean() # iou loss
def bbox_iou(box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, eps=1e-9):
# Returns the IoU of box1 to box2. box1 is 4, box2 is nx4
box2 = box2.T
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if x1y1x2y2: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
else: # transform from xywh to xyxy
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[0] - box1[2] / 2, box1[0] + box1[2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[1] - box1[3] / 2, box1[1] + box1[3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[0] - box2[2] / 2, box2[0] + box2[2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[1] - box2[3] / 2, box2[1] + box2[3] / 2
# Intersection area
inter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# Union Area
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1 + eps
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1 + eps
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
iou = inter / union
if GIoU or DIoU or CIoU:
cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width
ch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height
if CIoU or DIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1
c2 = cw ** 2 + ch ** 2 + eps # convex diagonal squared
rho2 = ((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2 +
(b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4 # center distance squared
if DIoU:
return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU
elif CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47
v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * torch.pow(torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1), 2)
with torch.no_grad():
alpha = v / ((1 + eps) - iou + v)
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + v * alpha) # CIoU
else: # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf
c_area = cw * ch + eps # convex area
return iou - (c_area - union) / c_area # GIoU
else:
return iou # IoU
2、置信度损失和类损失
yolov5代码用nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss或FocalLoss评价目标框和预测框的类损失和置信度损失,本节一一介绍这两个损失函数。
- nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss:
首先对预测输出作sigmoid变换,然后求变换后的结果与真实值的二值交叉熵.
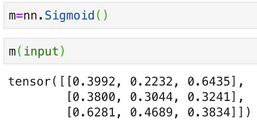
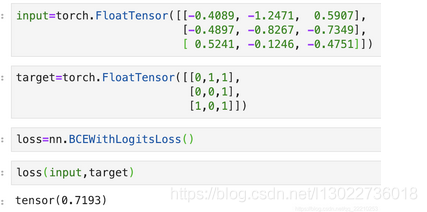
假设预测输出是3分类,预测输出:

预测输出sigmoid变换:
假设真实输出是:
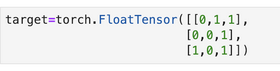
两者的二值交叉熵的计算方法:

接口函数验证下上面的结果:
- FocalLoss损失:
FocalLoss损失考虑的是:目标检测中正负样本严重不均衡的一种策略。该损失函数的设计思想类似于boosting,降低容易分类的样本对损失函数的影响,注重较难分类的样本的训练.
简而言之,FocalLoss更加关注的是比较难分的样本,何谓难分?若某一个真实类预测的概率只有0.2,我们认为它比较难分,相反若该真实类的预测概率是0.95,则容易分类.
FocalLoss通过提高难分类别的损失函数来实现,公式如下:
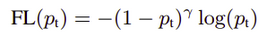
图像如下:
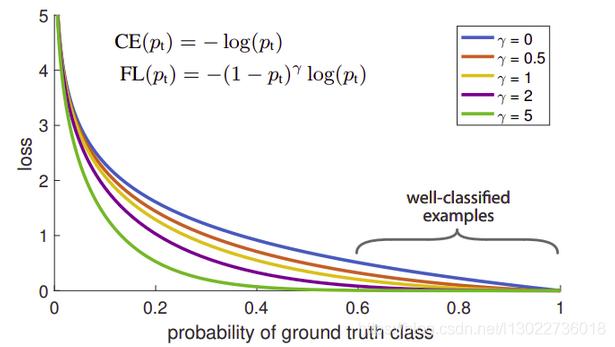
可以看出预测真实类概率越大,则损失函数越小,即实现了之前的想法.
为了能够平衡正负样本的重要性,我们可以给各个类别添加一个权重常数 α ,比如想使正样本初始权重为0.8,负样本就为0.2.
代码实现为:
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
# Wraps focal loss around existing loss_fcn(), i.e. criteria = FocalLoss(nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(), gamma=1.5)
def __init__(self, loss_fcn, gamma=1.5, alpha=0.25):
super(FocalLoss, self).__init__()
self.loss_fcn = loss_fcn # must be nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
self.gamma = gamma
self.alpha = alpha
self.reduction = loss_fcn.reduction
self.loss_fcn.reduction = 'none' # required to apply FL to each element
def forward(self, pred, true):
loss = self.loss_fcn(pred, true)
# p_t = torch.exp(-loss)
# loss *= self.alpha * (1.000001 - p_t) ** self.gamma # non-zero power for gradient stability
# TF implementation https://github.com/tensorflow/addons/blob/v0.7.1/tensorflow_addons/losses/focal_loss.py
pred_prob = torch.sigmoid(pred) # prob from logits
p_t = true * pred_prob + (1 - true) * (1 - pred_prob)
alpha_factor = true * self.alpha + (1 - true) * (1 - self.alpha)
modulating_factor = (1.0 - p_t) ** self.gamma
loss *= alpha_factor * modulating_factor
if self.reduction == 'mean':
return loss.mean()
elif self.reduction == 'sum':
return loss.sum()
else: # 'none'
return loss
其中成员函数loss_fcn为nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss。
总结
加载全部内容