RateLimiter通过AOP方式进行限流
yellow_han 人气:0使用RateLimiter通过AOP方式进行限流
1、引入依赖
<!-- guava 限流 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>25.1-jre</version> </dependency>
2、自定义注解
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ServiceLimit {
String description() default "";
}3、AOP实现类
@Component
@Scope
@Aspect
public class LimitAspect {
每秒只发出5个令牌,此处是单进程服务的限流,内部采用令牌捅算法实现
private static RateLimiter rateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(5.0);
//Service层切点 限流
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.itstyle.seckill.common.aop.ServiceLimit)")
public void ServiceAspect() {
}
@Around("ServiceAspect()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Boolean flag = rateLimiter.tryAcquire();
Object obj = null;
try {
if(flag){
obj = joinPoint.proceed();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
}4、使用
@Override
@ServiceLimit
@Transactional
public Result startSeckil(long seckillId,long userId) {
//todo 操作
}SpringBoot之限流
限流的基础算法
令牌桶和漏桶
- 漏桶算法 的实现往往依赖于队列,请求到达如果队列未满则直接放入队列,然后有一个处理器按照固定频率从队列头取出请求进行处理。如果请求量大,则会导致队列满,那么新来的请求就会被抛弃。
- 令牌桶算法 则是一个存放固定容量令牌的桶,按照固定速率往桶里添加令牌。桶中存放的令牌数有最大上限,超出之后就被丢弃或者拒绝。当流量或者网络请求到达时,每个请求都要获取一个令牌,如果能够获取到,则直接处理,并且令牌桶删除一个令牌。如果获取不到,该请求就要被限流,要么直接丢弃,要么在缓冲区等待。
令牌桶和漏桶对比
- 令牌桶是按照固定速率往桶中添加令牌,请求是否被处理需要看桶中令牌是否足够,当令牌数减为零时则拒绝新的请求;漏桶则是按照常量固定速率流出请求,流入请求速率任意,当流入的请求数累积到漏桶容量时,则新流入的请求被拒绝;
- 令牌桶限制的是平均流入速率,允许突发请求,只要有令牌就可以处理,支持一次拿3个令牌,4个令牌;漏桶限制的是常量流出速率,即流出速率是一个固定常量值,比如都是1的速率流出,而不能一次是1,下次又是2,从而平滑突发流入速率;
- 令牌桶允许一定程度的突发,而漏桶主要目的是平滑流出速率;
Guava RateLimiter
1.依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>28.1-jre</version> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
2.示例代码
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class RequestInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
// 根据字符串分不同的令牌桶, 每天自动清理缓存
private static LoadingCache<String, RateLimiter> cachesRateLimiter = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000) //设置缓存个数
/**
* expireAfterWrite是在指定项在一定时间内没有创建/覆盖时,会移除该key,下次取的时候从loading中取
* expireAfterAccess是指定项在一定时间内没有读写,会移除该key,下次取的时候从loading中取
* refreshAfterWrite是在指定时间内没有被创建/覆盖,则指定时间过后,再次访问时,会去刷新该缓存,在新值没有到来之前,始终返回旧值
* 跟expire的区别是,指定时间过后,expire是remove该key,下次访问是同步去获取返回新值;
* 而refresh则是指定时间后,不会remove该key,下次访问会触发刷新,新值没有回来时返回旧值
*/
.expireAfterAccess(1, TimeUnit.HOURS)
.build(new CacheLoader<String, RateLimiter>() {
@Override
public RateLimiter load(String key) throws Exception {
// 新的字符串初始化 (限流每秒2个令牌响应)
return RateLimiter.create(2);
}
});
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
log.info("request请求地址path[{}] uri[{}]", request.getServletPath(), request.getRequestURI());
try {
String str = "hello";
// 令牌桶
RateLimiter rateLimiter = cachesRateLimiter.get(str);
if (!rateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
System.out.println("too many requests.");
return false;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 解决拦截器的异常,全局异常处理器捕获不到的问题
request.setAttribute("exception", e);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/error").forward(request, response);
}
return true;
}
}
3.测试
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping
public Result test2(){
System.out.println("1111");
return new Result(true,200,"");
}
}http://localhost:8080/user/
如果没有result类,自己可以随便返回个字符串
4.测试结果
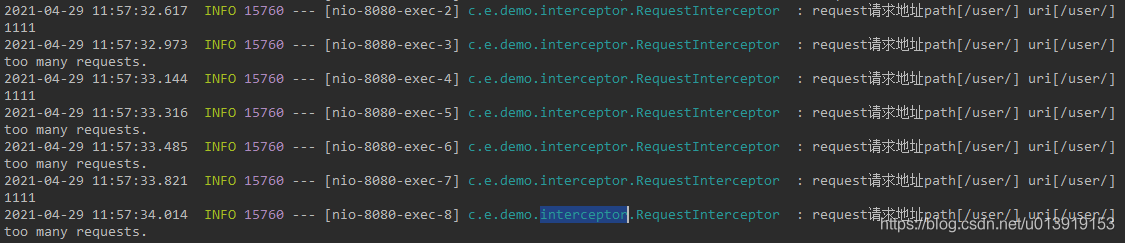
其他
创建
RateLimiter提供了两个工厂方法:
- 一个是平滑突发限流
RateLimiter r = RateLimiter.create(5); //项目启动,直接允许5个令牌
- 一个是平滑预热限流
RateLimiter r = RateLimiter.create(2, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //项目启动后3秒后才会到达设置的2个令牌
缺点
RateLimiter只能用于单机的限流,如果想要集群限流,则需要引入redis或者阿里开源的sentinel中间件。
TimeUnit.SECONDS);` //项目启动后3秒后才会到达设置的2个令牌
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容