解读调用jupyter notebook文件内的函数一种简单方法
AlexInML 人气:0调用jupyter notebook文件内的函数一种简单方法
python开发环境jupyter notebook良好的交互式和模块化受到很多python开发人员的青睐,但是jupyter notebook是以json格式保存文件内容的,而不是python文件那样的普通格式,所以不能直接被python解析器解析,如何调用.ipynb中的module也成为一个问题。
本文介绍一种方法,使得只要在我们的工作目录下放置一个python文件,就可以正常调用其他jupyter notebook文件。
Jupyter Notebook官网介绍了一种简单的方法:http://jupyter-notebook.readthedocs.io/en/latest/examples/Notebook/Importing Notebooks.html
添加jupyter notebook解析文件
首先,创建一个python文件,例如Ipynb_importer.py,代码如下:
import io, os,sys,types
from IPython import get_ipython
from nbformat import read
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
class NotebookFinder(object):
"""Module finder that locates Jupyter Notebooks"""
def __init__(self):
self.loaders = {}
def find_module(self, fullname, path=None):
nb_path = find_notebook(fullname, path)
if not nb_path:
return
key = path
if path:
# lists aren't hashable
key = os.path.sep.join(path)
if key not in self.loaders:
self.loaders[key] = NotebookLoader(path)
return self.loaders[key]
def find_notebook(fullname, path=None):
"""find a notebook, given its fully qualified name and an optional path
This turns "foo.bar" into "foo/bar.ipynb"
and tries turning "Foo_Bar" into "Foo Bar" if Foo_Bar
does not exist.
"""
name = fullname.rsplit('.', 1)[-1]
if not path:
path = ['']
for d in path:
nb_path = os.path.join(d, name + ".ipynb")
if os.path.isfile(nb_path):
return nb_path
# let import Notebook_Name find "Notebook Name.ipynb"
nb_path = nb_path.replace("_", " ")
if os.path.isfile(nb_path):
return nb_path
class NotebookLoader(object):
"""Module Loader for Jupyter Notebooks"""
def __init__(self, path=None):
self.shell = InteractiveShell.instance()
self.path = path
def load_module(self, fullname):
"""import a notebook as a module"""
path = find_notebook(fullname, self.path)
print ("importing Jupyter notebook from %s" % path)
# load the notebook object
with io.open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
nb = read(f, 4)
# create the module and add it to sys.modules
# if name in sys.modules:
# return sys.modules[name]
mod = types.ModuleType(fullname)
mod.__file__ = path
mod.__loader__ = self
mod.__dict__['get_ipython'] = get_ipython
sys.modules[fullname] = mod
# extra work to ensure that magics that would affect the user_ns
# actually affect the notebook module's ns
save_user_ns = self.shell.user_ns
self.shell.user_ns = mod.__dict__
try:
for cell in nb.cells:
if cell.cell_type == 'code':
# transform the input to executable Python
code = self.shell.input_transformer_manager.transform_cell(cell.source)
# run the code in themodule
exec(code, mod.__dict__)
finally:
self.shell.user_ns = save_user_ns
return mod
sys.meta_path.append(NotebookFinder())
调用jupyter notebook module
在我们的jupyter notebook文件里调用Ipynb_importer.py,接下来我们就可以像调用普通python文件一样调用其他.ipynb文件里的module了,例如有一个IpynbModule.ipynb文件,里面定义了一个foo函数:
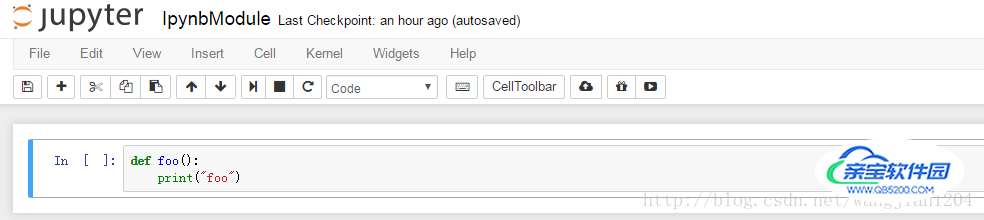
调用例子如下:
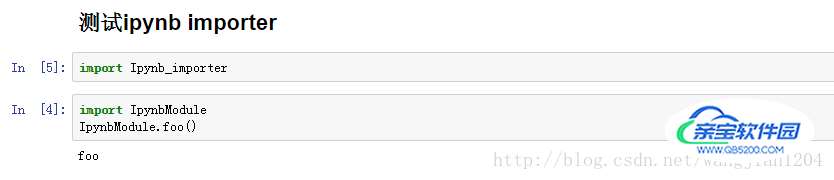
只要在我们的工作目录下放置Ipynb_importer.py文件,就可以正常调用所有的jupyter notebook文件。
这种方法的本质就是使用一个jupyter notenook解析器先对.ipynb文件进行解析,把文件内的各个模块加载到内存里供其他python文件调用。
参考资料:
http://jupyter-notebook.readthedocs.io/en/latest/examples/Notebook/Importing Notebooks.html
jupyter Notebook魔法函数
魔法函数
使用魔法函数可以简单的实现一些单纯python要很麻烦才能实现的功能。
| 符号 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| %: | 行魔法函数,只对本行代码生效。 |
| %%: | Cell魔法函数,在整个Cell中生效,必须放于Cell首行。 |
| %lsmagic: | 列出所有的魔法函数 |
| %magic | 查看各个魔法函数的说明 |
| ? | 后面加上魔法函数名称,可以查看该函数的说明 |
一些常用魔法函数的示例:
| 魔法函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| %%writefile | 调用外部python脚本 |
| %run | 调用外部python脚本 |
| %timeit | 测试单行语句的执行时间 |
| %%timeit | 测试整个单元中代码的执行时间 |
| % matplotlib inline | 显示 matplotlib 包生成的图形 |
| %%writefile | 写入文件 |
| %pdb | 调试程序 |
| %pwd | 查看当前工作目录 |
| %ls | 查看目录文件列表 |
| %reset | 清除全部变量 |
| %who | 查看所有全局变量的名称,若给定类型参数,只返回该类型的变量列表 |
| %whos | 显示所有的全局变量名称、类型、值/信息 |
| %xmode Plain | 设置为当异常发生时只展示简单的异常信息 |
| %xmode Verbose | 设置为当异常发生时展示详细的异常信息 |
| %debug bug | 调试,输入quit退出调试 |
| %env | 列出全部环境变量 |
注意这些命令是在Python kernel中适用的,其他 kernel 不一定适用
magic函数主要包含两大类,一类是行魔法(Line magic)前缀为%,一类是单元魔法(Cell magic)前缀为%%
%%writefile调用外部python脚本%run调用外部python脚本%timeit测试单行语句的执行时间%%timeit测试整个单元中代码的执行时间% matplotlib inline显示 matplotlib 包生成的图形%%writefile写入文件%pdb调试程序%pwd查看当前工作目录%ls查看目录文件列表%reset清除全部变量%who查看所有全局变量的名称,若给定类型参数,只返回该类型的变量列表%whos显示所有的全局变量名称、类型、值/信息
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容